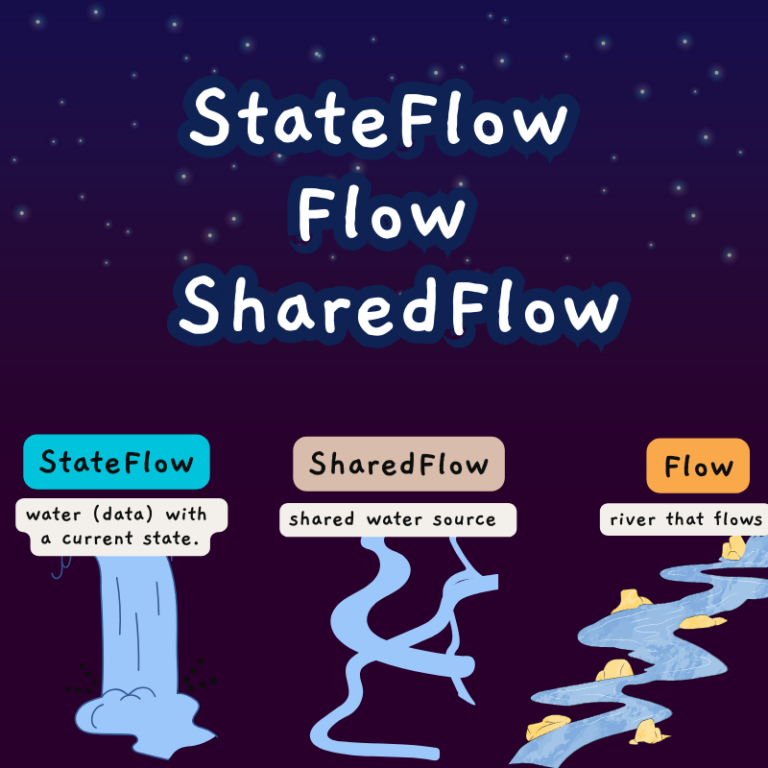
Kotlin Scope Functions Best Practices with 10 Coding Challenges

What is a scope function in Kotlin? In Kotlin, scope functions are a set of functions that allow concise and expressive ways to operate on objects within a certain scope. There are five main scope functions in Kotlin: let, run,…