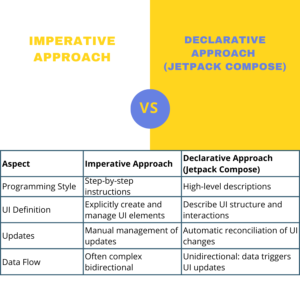
Table of Contents
Kotlin Variables and Data Types
Variables are like containers that can hold different types of information. Data types specify what kind of information a variable can hold.
In this tutorial, we’ll start with the basics: setting up your development environment and understanding variables and data types, all while using real-life scenarios to help you make connections.
Setting Up Your Development Environment
Before we dive into the exciting world of Kotlin, you’ll need a development environment to work in. Here’s how you can set it up:
Step 1: Install Java Development Kit (JDK)
Kotlin runs on top of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), so you’ll need to install the Java Development Kit (JDK) first. Head over to the Oracle JDK website or OpenJDK to download and install the latest version of JDK suitable for your operating system.
Step 2: Install Kotlin
Once you have the JDK installed, you can now install Kotlin. The easiest way to do this is by using a build tool like Gradle or Maven. If you’re new to these tools, don’t worry; they make setting up and managing dependencies a breeze.
For Gradle, add the following to your build.gradle file:
dependencies {
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib"
}
Step 3: Choose an IDE
An Integrated Development Environment (IDE) can make your coding journey much more enjoyable. Two popular options for Kotlin development are IntelliJ IDEA and Android Studio. IntelliJ IDEA is a general-purpose IDE, while Android Studio is tailored for Android app development.
Once you have your development environment set up, let’s move on to the fun part – variables and data types.
Variables and Data Types in Kotlin
| Data Type | Description | Example Values |
|---|---|---|
| Int | Whole numbers | 1, 42, -10 |
| Double | Decimal numbers | 3.14, -0.5, 2.0 |
| Float | Floating-point numbers with less precision | 3.14f, -0.5f |
| Long | Large whole numbers | 1000000L |
| Short | Small whole numbers | 10, -5 |
| Byte | Very small whole numbers | 1, -128 |
| String | Text or sequences of characters | “Hello, Kotlin!” |
| Char | Single characters | ‘A’, ‘$’ |
| Boolean | True or false values | true, false |
| Array | Fixed-size collection of items | [1, 2, 3] |
| List | Dynamic-size collection of items | listOf(1, 2, 3) |
| Set | Collection storing unique elements | setOf(1, 2, 2) |
| Map | Key-value pairs | mapOf(“key” to “value”) |
| Any | Can hold values of any type | Any, “Hello”, 42 |
| Unit | Represents absence of a meaningful value | Unit |
| Nothing | Represents a value or function that never exists | Nothing |
Imagine you’re building a virtual garden, and you need to keep track of different types of plants and their characteristics. In Kotlin, you can do this using variables and data types.
Variables
Variables are like containers that can hold different types of information. Let’s create a few variables to represent different plants in your garden.
val roseColor: String = "Red"
var sunflowerHeight: Double = 5.2
In the code above, val and var are keywords. val is used for read-only (immutable) variables, while var is used for mutable variables. You assigned a color to the roseColor variable and a height to the sunflowerHeight variable. The : String and : Double parts indicate the data types of these variables.
Data Types: Data types specify what kind of information a variable can hold. Here’s a real-life scenario to help you understand data types better.
Imagine you’re creating a simple weather app. You need to store the temperature, which can be in Celsius or Fahrenheit. Kotlin has built-in data types to handle these situations.
val temperatureInCelsius: Double = 25.5
val temperatureInFahrenheit: Double = 77.9
In this scenario, Double is the data type for both temperatureInCelsius and temperatureInFahrenheit. It allows us to store decimal values like temperatures.
In this scenario, Double is the data type for both temperatureInCelsius and temperatureInFahrenheit. It allows us to store decimal values like temperatures.
Summary:
- Variables are containers for storing information.
valcreates read-only (immutable) variables, whilevarcreates mutable variables.- Data types define the kind of information a variable can hold. In our weather app example, we used
Doubleto store temperature values.
Let’s use a real-life scenario to understand variables better:
Scenario: Shopping List
You are creating a shopping list for groceries. Each item on your list is like a variable. Here’s how you could represent it in code:
item1 = "Apples"
item2 = "Milk"
item3 = "Bread"In this example, item1, item2, and item3 are variables, and they hold the names of the items you need to buy.
What Are Data Types in Kotlin?
In Kotlin, data types are a way of categorizing and defining the various kinds of data that your program can work with. Think of data types as labels that tell the computer how to treat different pieces of information.
Imagine you’re building a virtual garden, and you need to keep track of different types of plants and their characteristics. In Kotlin, you can do this using variables and data types.
Data types define the kind of data a variable can hold. Different data types are designed to handle various types of information. Let’s explore some common data types:
Primitive Data Types
Primitive data types in Kotlin are the most basic building blocks for storing simple values. They are directly supported by the programming language and don’t require any special libraries or packages. Here are some common primitive data types in Kotlin:
| Data Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
Int | Integer values | 42 |
Double | Floating-point numbers | 3.14 |
Boolean | Represents true or false | true |
Char | Single characters | 'A' |
String | Textual data | "Hello" |
Short | Short integers | 32767 |
Long | Long integers | 9223372036854 |
Float | Single-precision floating-point numbers | 3.14f |
Non-Primitive Data Types
Non-primitive data types, also known as reference types, are more complex data structures built upon primitive data types. They are not directly supported by the language but are created using classes and objects. Common non-primitive data types include:
| Data Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Arrays | Ordered collections of items of the same type. Arrays have a fixed size. | val numbers: Array<Int> = arrayOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5) |
| Lists | Dynamic collections of items that can change in size. Lists can hold items of different types. | val fruits: List<String> = listOf("Apple", "Banana", "Orange") |
| Sets | Unordered collections of unique items. Sets do not allow duplicate elements. | val uniqueNumbers: Set<Int> = setOf(1, 2, 3, 2, 4) |
| Maps | Key-value pairs for storing and retrieving data. Each key is associated with a unique value. | val studentGrades: Map<String, Int> = mapOf("Alice" to 95, "Bob" to 88, "Charlie" to 75) |
| Classes | Custom data types that you define in your program. Classes can have properties and methods. | kotlin class Person(val name: String, val age: Int)<br> val person1: Person = Person("John", 30) |
1. Integer (Int)
An Int is like a container for whole numbers, like counting the number of apples.
val numberOfApples: Int = 5
2. Double
A Double is used for numbers with decimals, like measuring the weight of something.
val weightOfBox: Double = 3.5
3. String
A String is like a container for text, like a label on a jar of peanut butter.
val userName: String = "Alice"
4. Boolean
A Boolean is like a switch that can be either “on” (true) or “off” (false), like a light switch.
val isRaining: Boolean = false
5. List
A List is like a container that holds a collection of items, like a shopping list.
Kotlin is a modern, statically-typed programming language that runs on the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). It has a rich standard library, including data structures like lists. In Kotlin, a list is an ordered collection of elements that can contain duplicates. Lists are part of the Kotlin Standard Library and are represented by the List interface. Lists in Kotlin are immutable by default, meaning their contents cannot be changed after they are created. If you need a mutable list, you can use MutableList.
There are three main types of lists: List, MutableList, and Immutable lists created using the listOf() function. Each of these has different characteristics and use cases:
val shoppingList: List<String> = listOf("Apples", "Milk", "Bread")
Immutable List
– The Museum Exhibit
Imagine visiting a museum where precious artifacts are displayed. These artifacts are beautiful and historically significant. However, you can’t touch them or change their position. That’s precisely what an immutable list in Kotlin is like.
Example: Suppose you have a list of famous landmarks:
val landmarks = listOf("Eiffel Tower", "Great Wall of China", "Taj Mahal")
In this case, you cannot add, remove, or modify landmarks once the list is created. It’s like a museum exhibit where the artifacts (landmarks) are fixed.
Immutable List: Use when you have a fixed set of items that should not change after creation. Like the artifacts in a museum, these items are set in stone.
- Immutable List (Created Using
listOf()): - In addition to the
Listinterface, Kotlin provides a convenient way to create immutable lists using thelistOf()function. - This is essentially the same as using
List, but it’s a common pattern in Kotlin to uselistOf()for creating immutable lists to make the intention clear.
Mutable List
– The Dynamic Grocery List
Now, picture your grocery shopping list. You start with a basic list, but you might add, remove, or modify items as you go through the store. A mutable list in Kotlin is just like that.
Example: You create a mutable shopping list:
val shoppingList = mutableListOf("Apples", "Bread", "Milk")
As you shop, you can easily add more items (e.g., “Eggs,” “Cereal”) or change your mind and remove items. The list adapts to your needs, just like your grocery list.
As you shop, you can easily add more items (e.g., “Eggs,” “Cereal”) or change your mind and remove items. The list adapts to your needs, just like your grocery list.
MutableListis an interface in Kotlin’s standard library as well.- It also represents an ordered collection of elements.
- Lists created using
MutableListare mutable, meaning that you can add, remove, and modify elements after creation. - You can use
mutableListOf()to create a mutable list.
In Kotlin, a List and an immutable list created using listOf() are very similar but not exactly the same.
- List (kotlin.collections.List):
Listis an interface in Kotlin’s standard library.- It represents an ordered collection of elements.
- Lists created using the
Listinterface can be both mutable and immutable, depending on the concrete implementation used. - The mutability depends on the specific implementation you use, such as
mutableListOf()for mutable lists andlistOf()for immutable lists.
- Immutable List (Created with
listOf()):- An immutable list is created using the
listOf()function. - It is also a
Listinterface, but it specifically emphasizes immutability. - Lists created with
listOf()are immutable, meaning that once you create them, you cannot add, remove, or modify elements.
- An immutable list is created using the
When you see “List” in Kotlin, it’s likely referring to an immutable list created with listOf(). The key point is that lists created with listOf() are always immutable, while lists created using mutableListOf() are explicitly mutable and allow modifications.
KArray
In Kotlin, an array is a fixed-size, ordered collection of elements of the same type. Arrays are useful for storing and working with a set of values, and they can be used for various purposes in programming. Here’s how you can declare, initialize, and work with arrays in Kotlin:
Declaring an Array
val numbers = arrayOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
In this code, we declare an array called numbers that contains five integers. You can change the values and the number of elements as needed.
Accessing Array Elements
val firstNumber = numbers[0]
This sets the firstNumber variable to 1, which is the first element in the array.
Modifying Array Elements
numbers[1] = 10
Now, the numbers array will be [1, 10, 3, 4, 5].
Iterating Through an Array
for (number in numbers) {
println(number)
}
This loop will print:
1
10
3
4
5Problem 1: Find the Sum of All Elements in an Array
Problem Statement: Given an array of integers, find the sum of all elements in the array
fun main() {
val numbers = arrayOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
var sum = 0
for (number in numbers) {
sum += number
}
println("The sum of all elements is: $sum")
}
In this solution, we initialize a variable sum to zero and then use a for loop to iterate through the numbers array. We add each element to the sum variable, effectively calculating the sum of all elements in the array. sum += number is shorthand for sum = sum + number. It adds the value of number to the current value of sum and updates the sum variable with the new result.
Problem 2: Find the Maximum Element in an Array
Problem Statement: Given an array of integers, find the maximum element in the array.
fun main() {
val numbers = arrayOf(12, 6, 8, 15, 3)
var max = numbers[0]
for (number in numbers) {
if (number > max) {
max = number
}
}
println("The maximum element is: $max")
}
In this solution, we initialize the max variable with the first element of the numbers array. Then, we iterate through the array and compare each element with the current maximum (max). If we find an element greater than the current maximum, we update the max variable with the new maximum value.
Problem 3: Check if an Array is Sorted in Ascending Order
Problem Statement: Given an array of integers, check if it is sorted in ascending order.
fun isSortedAscending(arr: Array<Int>): Boolean {
for (i in 1 until arr.size) {
if (arr[i] < arr[i - 1]) {
return false
}
}
return true
}
Kotlin Variables and Data Types Questions
1. What is a variable in Kotlin?
- Answer: In Kotlin, a variable is a container that can hold data. It is used to store and manipulate values within a program.
2. How do you declare a variable in Kotlin?
- Answer: You can declare a variable in Kotlin using the
valkeyword for read-only (immutable) variables and thevarkeyword for mutable variables.
3. What is the difference between val and var in Kotlin?
- Answer: Variables declared with
valare read-only and cannot be reassigned after their initial value is set. Variables declared withvarare mutable and can be reassigned.
4. What are the basic data types in Kotlin?
- Answer: Kotlin has a variety of basic data types, including
Int,Double,Float,Char,Boolean,String, andLong, among others.
5. How do you define a constant in Kotlin?
- Answer: You can define a constant in Kotlin using the
valkeyword. Constants are read-only and cannot be changed after they are initialized.
6. How can you convert one data type to another in Kotlin?
- Answer: In Kotlin, you can use explicit type casting to convert one data type to another. For example:
val intVar: Int = 42
val doubleVar: Double = intVar.toDouble()
8. How can you specify a custom data type in Kotlin? – Answer: You can create custom data types in Kotlin by defining classes or data classes. These classes allow you to encapsulate data and behavior into your own types.
Feel free to follow and join my email list at no cost. Don’t miss out — sign up now!
Please check out my earlier blog post for more insights. Happy reading!
The Innovative Fundamentals of Android App Development in 2023
How to learn Android App Development in 2023 – Full Guide For Beginners using Kotlin Language
Ultimate Guideline on How to Use ViewModel Design Pattern
What is the Repository Pattern in Android? A Comprehensive Guide
What is ViewModel in Android? A Good Guide for Beginners
The Innovative Fundamentals of Android App Development in 2023
How to Say Goodbye to Activity Lifecycle and Say Hello to Compose Lifecycle ?
How to Monitor/Observe Network Availability for Android Projects
Exploring Sealed Class vs Enum in Kotlin Which is Best for Your Code?