
Kotlin Control Flow and Operations Best Practices. Logical operators in Kotlin are essential for controlling the flow of your code and making decisions based on certain conditions.

Discover the magic of thinking functionally as we shift our mindset from step-by-step procedures to elegant transformations and computations
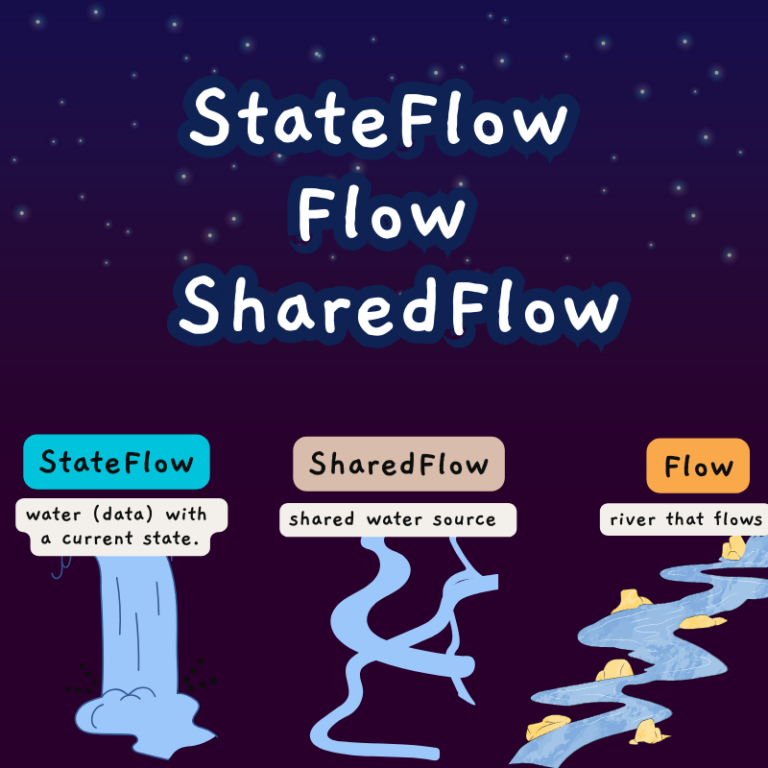
In Android development with Kotlin and Jetpack Compose, you often work with different types of data flows and observables to handle UI updates efficiently. Three commonly used options are Flow, SharedFlow, and StateFlow. Here, I'll provide a simple code example for each and explain every line of code for a non-technical person.

Dependency Injection (DI) is a design pattern and a software development technique used in object-oriented programming to manage the dependencies between different components or objects in a more flexible and maintainable way.
In a software application, various classes or components often need to collaborate and interact with each other. These interactions create dependencies, which can make the code less modular and harder to maintain

Handling nulls in Kotlin is crucial to prevent null pointer exceptions and write robust code. Kotlin provides several mechanisms to deal with nulls effectively
Handling null values in Kotlin is an important skill,
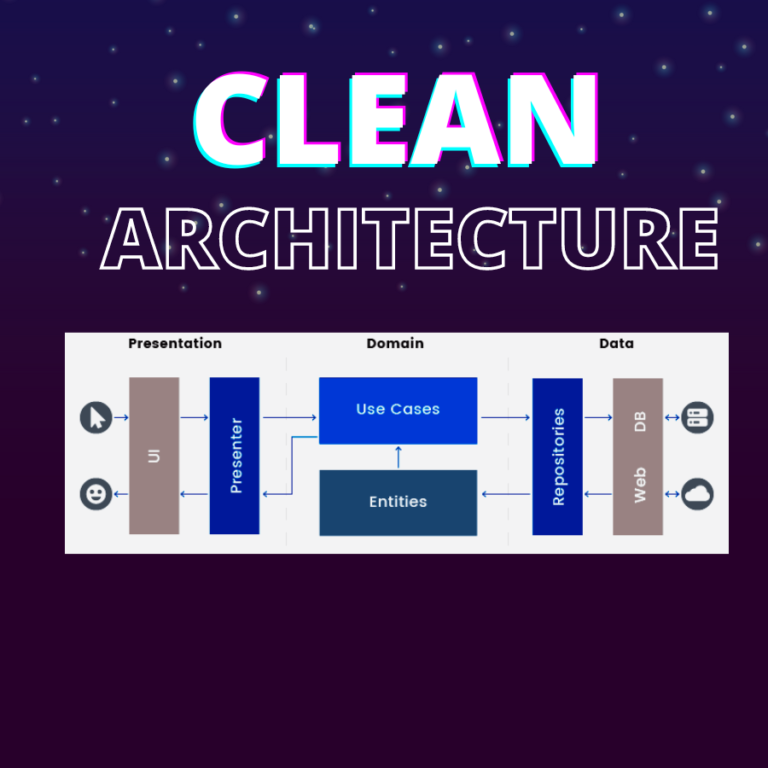
Discover the principles and benefits of Clean Architecture for developing software systems that are modular, maintainable, and adaptable. Learn how this architectural approach enhances code quality and promotes separation of concerns.
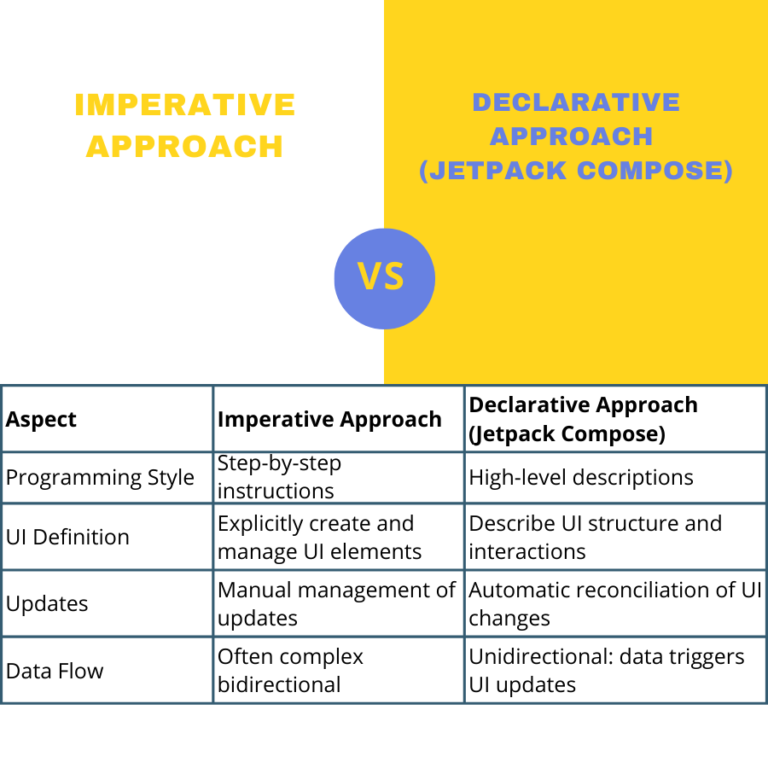
Explore the key differences between Imperative and Declarative UI Development using Jetpack Compose. Learn how these approaches impact app development and user interfaces. Get insights, comparisons, and FAQs answered in this comprehensive guide.

Learn about the differences between mutable state and state management libraries in Android development. Understand how these concepts impact app performance and user experience. Explore the advantages of using state management libraries for efficient and maintainable code.

Explore the differences between Static and Companion Objects in Kotlin. Learn how they work, their use cases, and why they matter in Kotlin programming. Find answers to FAQs and gain insights from experts.
Sealed classes are a bit like having a magical box that can hold different kinds of things, not just crayons. Inside this box, you can have crayons of different colors, but you can also have stickers and even small toys. Each thing in the box might look different and do different stuff. So, sealed classes let you have a special box where you can keep crayons and more, and each thing inside can be special and have its own abilities.










